.Net Project Manager-ASP.NET Core interview questions and answer
✅ SECTION 1: TECHNICAL QUESTIONS (ASP.NET Core / .NET Stack)
1. Q: What are the key features of ASP.NET Core that differentiate it from ASP.NET MVC 5?
A:
-
Cross-platform support (.NET Core runs on Windows, Linux, and macOS)
-
Unified MVC and Web API into a single framework
-
Dependency Injection is built-in
-
Modular pipeline via middleware
-
Performance improvements (Kestrel web server)
-
Configuration via appsettings.json and environment-based configs
-
Hosting independence (can be hosted in IIS, Kestrel, Docker, etc.)
2. Q: How do you handle Dependency Injection in ASP.NET Core?
A:
ASP.NET Core has built-in support for DI. Services are registered in Startup.cs under ConfigureServices. For example:
You can then inject the service via constructor injection:
3. Q: How would you design a scalable ASP.NET Core application?
A:
-
Use clean architecture or onion architecture
-
Apply SOLID principles
-
Use caching (e.g., Redis)
-
Enable horizontal scaling with stateless services
-
Implement asynchronous programming
-
Use AutoMapper, MediatR, and Swagger for best practices
-
Separate concerns with microservices or modular monoliths
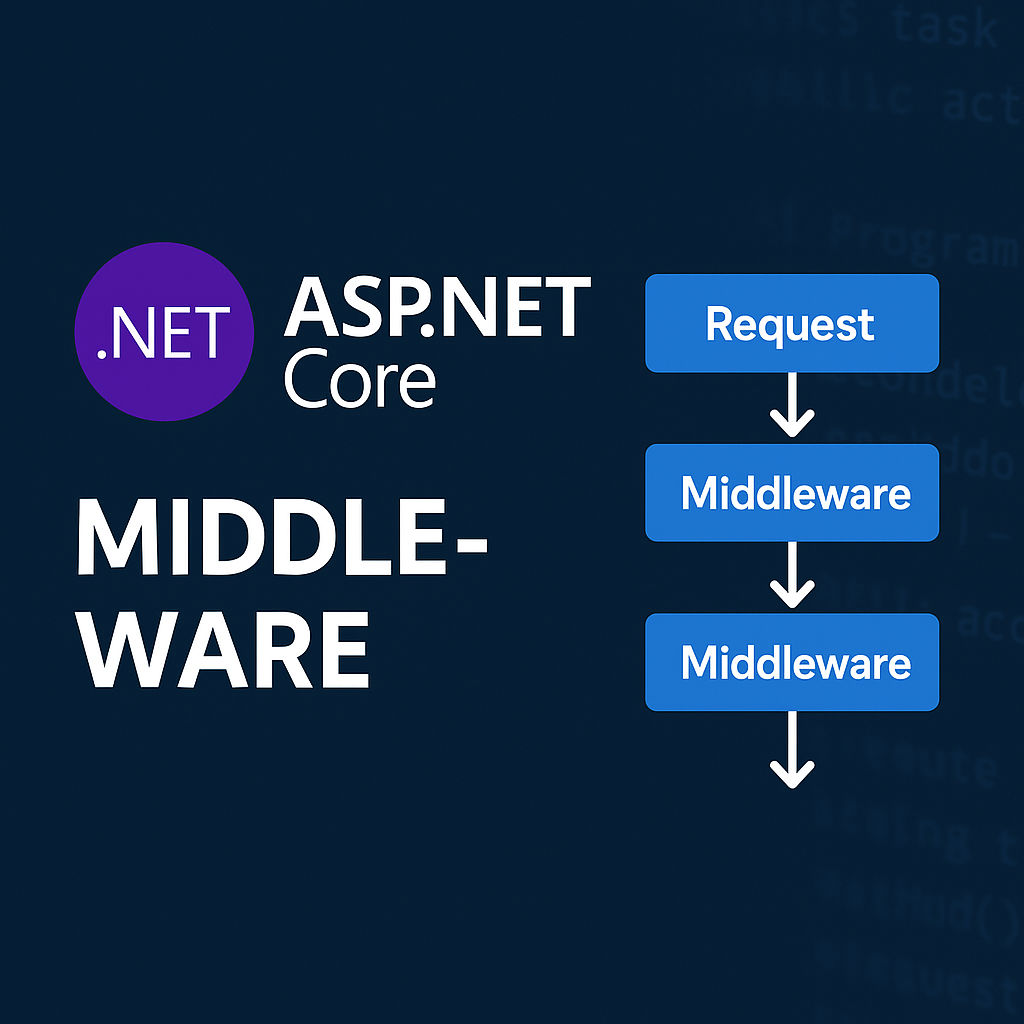
4. Q: What is Middleware in ASP.NET Core? Give examples.
A:
Middleware are components that form the request/response pipeline. They can handle requests and responses. Examples:
-
UseAuthentication() -
UseAuthorization() -
UseExceptionHandler() -
Custom middleware for logging or auditing
5. Q: How do you implement Logging and Monitoring in ASP.NET Core?
A:
-
Use built-in
ILogger<T>for logging -
Integrate with Serilog, NLog, or Application Insights
-
Add structured logging (e.g., JSON format)
-
Use tools like ELK Stack, Prometheus, Grafana for monitoring
✅ SECTION 2: PROJECT MANAGEMENT & DELIVERY
6. Q: How do you manage delivery timelines in an Agile .NET project?
A:
-
Break down features into user stories and tasks
-
Use tools like JIRA, Azure Boards for sprint planning
-
Maintain a product backlog and prioritize based on business needs
-
Conduct daily standups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives
-
Track velocity and adjust capacity planning accordingly
7. Q: Describe your experience handling client communication and expectation management.
A:
-
I ensure regular communication through daily syncs, weekly reports, and demos
-
Set realistic expectations upfront and avoid overpromising
-
Use RAG status, highlight risks early
-
Document all decisions and changes via Change Requests (CRs)
8. Q: How do you ensure code quality and maintainability in a .NET project?
A:
-
Enforce code reviews and pull request workflows
-
Implement SonarQube or FxCop for static code analysis
-
Apply unit testing with xUnit/NUnit and aim for good coverage
-
Use CI/CD pipelines with automated builds and tests
-
Maintain proper documentation and use version control (Git)
9. Q: How do you estimate a .NET project?
A:
-
Break down into modules/features
-
Use Function Point Analysis, Planning Poker, or Story Points
-
Add buffer for risks, integrations, and unknowns
-
Review past sprint velocities for estimation accuracy
-
Validate estimates with the dev team and stakeholders
✅ SECTION 3: BEHAVIORAL & LEADERSHIP
10. Q: How do you handle conflicts between developers or with stakeholders?
A:
-
Identify the root cause through open discussion
-
Ensure everyone is heard—use active listening
-
Re-align to project goals and business outcomes
-
Escalate only if resolution is not possible at the team level
-
Promote a collaborative and respectful work culture
11. Q: How do you mentor and grow a .NET development team?
A:
-
Conduct code reviews and provide constructive feedback
-
Encourage developers to contribute to design discussions
-
Organize knowledge-sharing sessions
-
Assign stretch tasks to help them grow
-
Track growth using IDPs (Individual Development Plans)
12. Q: Have you managed a project migration from ASP.NET MVC to ASP.NET Core? What challenges did you face?
A:
Yes, challenges included:
-
Third-party packages not being .NET Core-compatible
-
Refactoring Web.config to new config model
-
Rewriting authentication/authorization with Identity or JWT
-
Updating legacy data access layers (e.g., from ADO.NET to EF Core)
-
Ensuring backward compatibility via staging environments and extensive testing